Ensuring the privacy and security of your Android phone hinges on understanding and adjusting various security settings, from the lock screen to app permissions and beyond.
This guide will navigate you through the essentials of Android security, highlighting the importance of encryption, managing access and permissions, and safeguarding your device against malicious threats.
Whether you're looking to secure your Google account, disable unwanted tracking, or encrypt your personal data, we'll cover the built-in security features Android offers and recommend using specific settings to protect your smartphone.
Step-by-step Guide for Enhancing Android Privacy and Security
Step 1: Update Your Device and Apps
Step 2: Review and Optimize App Permissions
Step 3: Enable a Strong Lock Screen
Step 4: Activate Find My Device
Step 6: Use Secure Communication Tools
Step 7: Opt for a Privacy-focused Browser and Search Engine
Step 8: Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Step 9: Disconnect from Google Services
Step 10: Consider Installing a Custom ROM
Step 1: Update Your Device and Apps
Regularly check for and install any available updates for both your Android operating system and all installed apps. This can typically be done through your device's settings menu for system updates and the Google Play Store for app updates.
For System Updates: Navigate to Settings > Select About Phone > Tap Check for Update > Install. If an update is available, you'll see an option to download and install it. It's recommended to do this over a Wi-Fi connection to avoid using your data allowance.
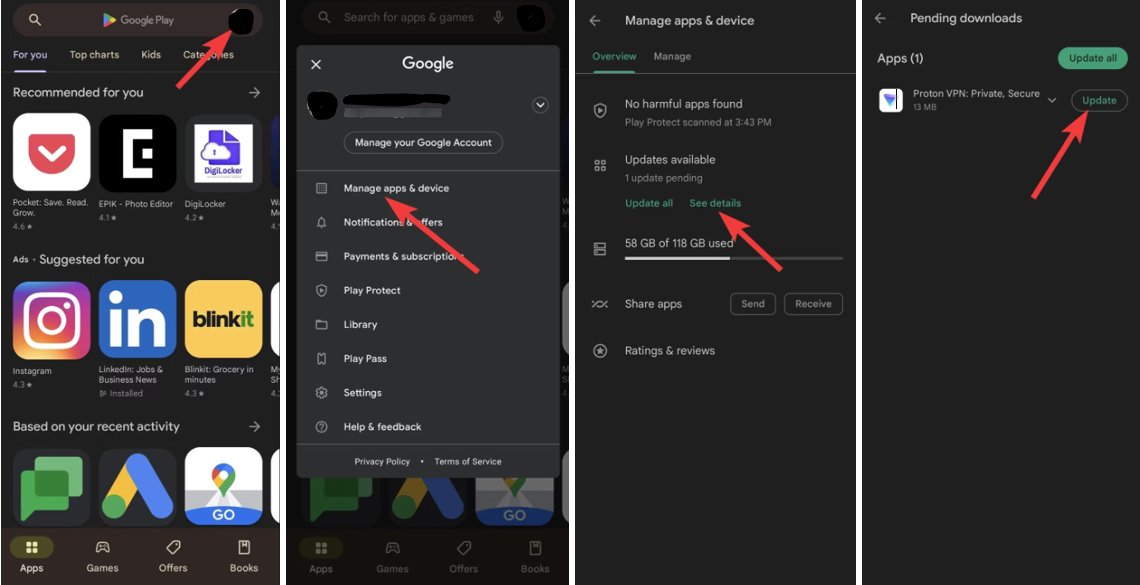
For App Updates: Open the Google Play Store app, tap on your profile icon at the top right corner, then tap on 'Manage apps & device'. Under 'Updates available', you can see which apps have updates. Tap 'Update all' to apply all available updates or select individual apps to update.
Tools and Examples:
Google Play Protect: Integrated into the Play Store, it continuously works to keep your device, data, and apps safe. It scans your device for potentially harmful apps from the Play Store or other sources and provides warnings about any detected dangers.

Security Software Apps: While not a direct tool for updating, apps like Avast Mobile Security or Bitdefender Antivirus Free can offer additional security layers by detecting malware or malicious activities on your device, which could signify an out-of-date app or system vulnerability.

Step 2: Review and Optimize App Permissions
Tools and Examples:
Bouncer: An app that temporarily grants permissions to apps and automatically revokes them after a certain period or when you exit the app. This is particularly useful for apps that you trust but only need to access specific data occasionally.
Privacy Dashboard: Available in Android 12 and later, this feature offers an overview of how often apps access particular permissions like location, camera, and microphone over the past 24 hours. It's an integrated tool that helps you understand which apps are frequently using sensitive permissions.
Step 3: Enable a Strong Lock Screen
Choosing a Strong Lock Type: Navigate to Settings > Security > Screen lock. You'll be presented with options including PIN, password, and pattern. While patterns are convenient, they're often less secure due to predictability and smudge patterns left on the screen. PINs and passwords offer higher security, especially when you use a complex combination.
Creating a Secure PIN or Password: Opt for a PIN with at least 6 digits or a password that combines letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid easily guessable PINs such as "123456" or "111111", and stay clear of passwords that contain personal information like birthdays or anniversaries.
Tools and Examples:
Smart Lock: For added convenience without compromising security, Android's Smart Lock feature can keep your device unlocked in trusted situations, like when you're at home or when the device is on your person. Find it under Settings > Security > Smart Lock. Remember, while Smart Lock offers convenience, it should be used judiciously to ensure it doesn't inadvertently weaken your security posture.
Lockdown Mode: This feature, available on newer Android versions, allows you to temporarily disable Smart Lock, fingerprint unlocking, and notifications on the lock screen. Activate it by holding down the power button and tapping "Lockdown" or through Settings > Display > Advanced > Lock screen display > Show lockdown option.
Step 4: Activate Find My Device
Enable Find My Device: Go to Settings > Security (or Google > Security) > Find My Device. Toggle the switch to the On position to activate this feature.
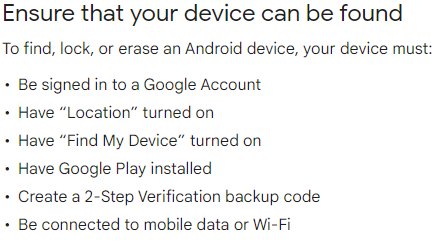
Verify Device Manager Access: For Find My Device to work correctly, it needs certain permissions. Ensure that the Find My Device app has the necessary permissions by checking under Settings > Apps & notifications > Advanced > Special app access > Device admin apps.
Tools and Examples:
Google Find My Device App: While the service is built into Android, Google also offers a Find My Device app available on the Play Store. This app can be used on another Android device to locate and manage your lost device remotely.
Third-party Security Apps: For those seeking additional features or alternatives to Google's offering, apps like Lookout and Prey provide device tracking, along with other security features such as photo capture of the thief, device health monitoring, and more.
Step 5: Install a VPN
Selecting a VPN Provider: Look for a reputable VPN provider that prioritizes privacy and security. Features to consider include a no-logs policy, strong encryption methods, and the availability of servers in multiple countries.
Installation and Setup: Once you've chosen a VPN provider, download their app from the Google Play Store. Follow the app's setup instructions to connect to a VPN server. Most apps feature a simple one-tap connection to secure your internet traffic.
Tools and Examples:
ProtonVPN: Known for its strong privacy stance, ProtonVPN offers a free tier with no data limits, making it a great option for those new to VPNs.
NordVPN: Offers a wide range of servers around the world, robust security features, and a user-friendly interface, making it a popular choice among VPN users.
ExpressVPN: Praised for its high speeds and strong encryption, ExpressVPN is a solid choice for streaming and downloading content securely.
Step 6: Use Secure Communication Tools
Choosing Encrypted Messaging Apps: Signal is widely recognized for its robust encryption protocols, ensuring that only the sender and recipient can read messages. Download the Signal app from the Google Play Store and follow the setup instructions to start securely messaging and calling your contacts.
Opting for Encrypted Email Services: ProtonMail offers end-to-end encryption for emails, meaning not even ProtonMail can access the content of your messages. Sign up for an account on their website or directly through their Android app, and use it for your sensitive email communications.
Tools and Examples:
Signal: Offers messaging, voice, and video calls with end-to-end encryption. It's open-source, allowing its security to be independently verified by experts.
ProtonMail: Provides encrypted email services with a user-friendly interface. It's based in Switzerland, benefiting from strong privacy laws.
Telegram (Secret Chats): While standard Telegram messages are not end-to-end encrypted, its "Secret Chats" feature offers this level of security for one-on-one conversations.

Step 7: Opt for a Privacy-focused Browser and Search Engine
Selecting a Privacy-focused Browser: Install a browser dedicated to protecting your online privacy. Firefox and Brave are two prominent examples that offer enhanced tracking protection and security features out of the box. You can download them directly from the Google Play Store.
Changing Your Search Engine: Within your chosen browser, navigate to the settings menu to change your default search engine to one that respects your privacy, such as DuckDuckGo. This search engine is known for not tracking user queries or creating profiles based on search history.
Tools and Examples:
Firefox: Offers robust privacy controls, including blocking third-party cookies by default and the ability to easily install privacy-enhancing extensions.
Brave: Built with privacy in mind, Brave automatically blocks ads and trackers, speeds up loading times, and offers features like Tor integration for browsing.
DuckDuckGo: Not just a search engine, DuckDuckGo also provides a mobile browser app that offers comprehensive privacy protection features, including tracker blocking and a privacy grade rating for websites.

Step 8: Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Activating 2FA for Your Google Account: Visit the Google Account security page, find the "2-Step Verification" section, and click on "Get Started." Follow the prompts to set up 2FA, choosing from methods like text message codes, authenticator apps, or backup codes.
Enabling 2FA on Other Services: Most online platforms, including social media, banking, and email services, now offer 2FA options. Typically found in the security settings of your account, these can usually be activated with just a few clicks. Look for terms like "Two-step verification," "Two-factor authentication," or "Extra security steps."
Tools and Examples
Authenticator Apps: Google Authenticator or Authy generate time-based codes used during the login process. Unlike SMS codes, authenticator apps are not vulnerable to SIM swap attacks, making them a more secure option for 2FA.
Hardware Security Keys: Devices like YubiKey offer a physical method of 2FA, requiring the key to be inserted into your computer or connected to your phone for access to be granted. This method is considered one of the most secure forms of 2FA.
Step 9: Disconnect from Google Services
Identify Essential Google Services: Assess which Google services you use and determine which ones you can replace with privacy-centric alternatives. Common services include Google Search, Gmail, Google Drive, and Google Maps.
Switch to Privacy-Focused Alternatives
Search Engine: Replace Google Search with DuckDuckGo or Startpage for private browsing experiences that don’t track your searches.
Email Service: Transition from Gmail to provider like ProtonMail, which offers end-to-end encrypted email services.
Cloud Storage: Consider switching from Google Drive to services like Nextcloud or Tresorit, which prioritize user privacy and data encryption.
Maps and Navigation: For maps, try alternatives like OsmAnd or MapQuest, which offer similar functionalities with more privacy.
Step 10: Consider Installing a Custom ROM
Research Compatible ROMs: Not all custom ROMs are compatible with every device. Start by researching which ROMs are available for your specific model. XDA Developers forums are a great resource for this information.
Choose a Privacy-Focused ROM: Select a ROM that prioritizes privacy.
LineageOS focuses on flexibility and customization while providing a clean operating system free from bloatware.
GrapheneOS emphasizes security enhancements and minimal Google integration for those wanting to sever ties with Google services.
CalyxOS offers a balanced approach with privacy features and optional Google services integration for those who need it.
Follow Detailed Installation Guides: Each ROM has specific installation requirements and steps. Official websites and forums like XDA Developers provide detailed guides. Ensure you follow them closely to avoid any issues during the installation process.
Tools and Examples:
TWRP (Team Win Recovery Project): A custom recovery required for flashing custom ROMs, providing a touchscreen-enabled interface for easy installation.
ADB (Android Debug Bridge): A versatile command-line tool that lets you communicate with your device for side-loading ROMs and apps.
Step 11: Implement Physical Security Measures
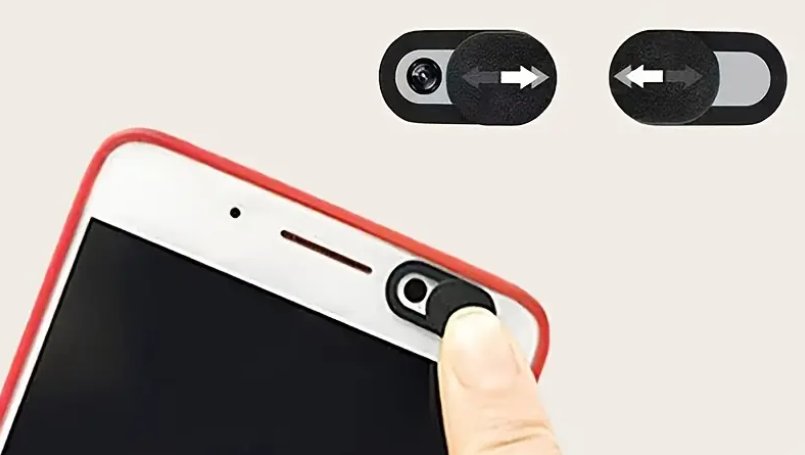
Camera Covers: Small, adhesive covers that slide or stick over your device's camera when not in use. These can be easily found online and are simple to apply and use. They provide a physical barrier against unwanted camera activation.

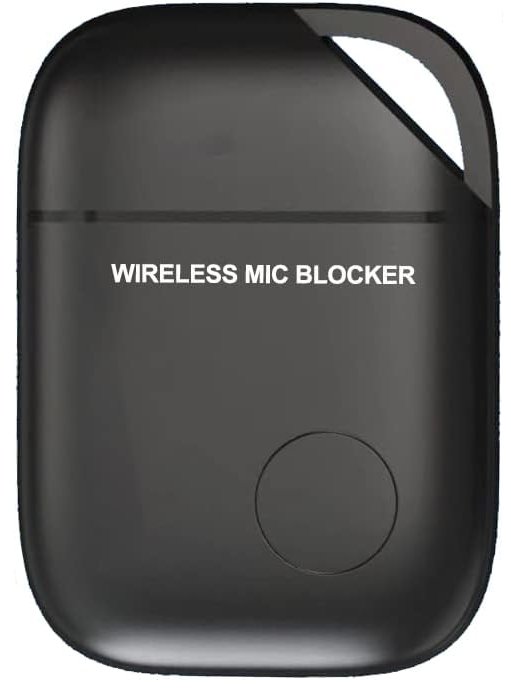
Microphone Blockers: These plug into your device's audio jack (or via an adapter for devices without a headphone jack) to physically block access to the microphone, preventing remote listening. Some products also simulate a microphone presence to fully block unauthorized audio capture.

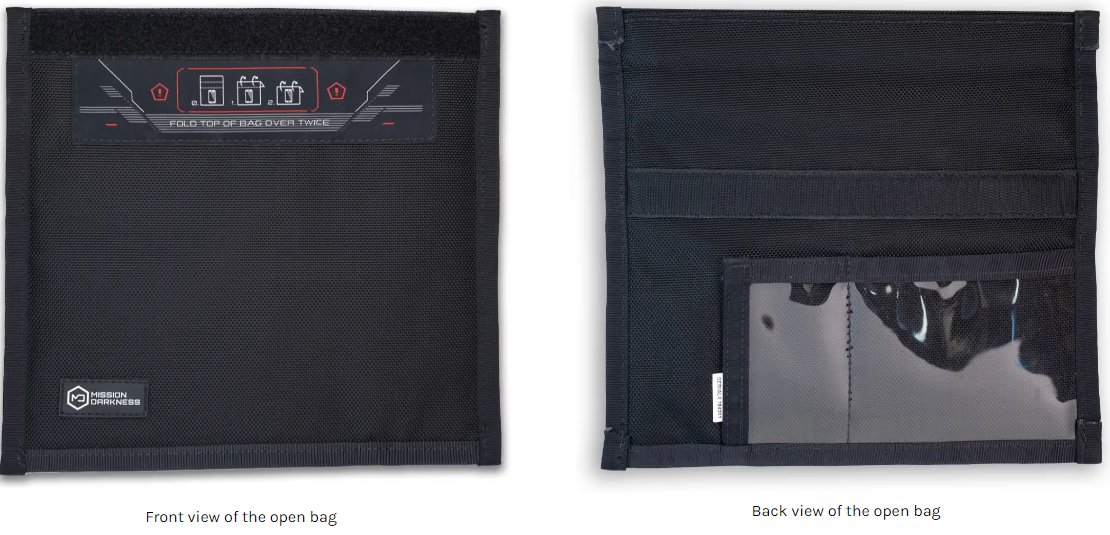
Faraday Bags: Special bags designed to block all wireless signals, including cellular, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and GPS. Placing your device in a Faraday bag when not in use ensures it cannot be tracked or remotely accessed.

Tools and Examples:
Camera Covers: Products like Webcam Cover Slide by CloudValley are slim and compatible with many devices, offering a physical shutter to block the camera.
Microphone Blockers: The Mic-Lock microphone blocker simulates a connected microphone, providing security against eavesdropping without interfering with your device's functionality.
Faraday Bags: The Mission Darkness Non-Window Faraday Bag for Phones blocks all wireless signals, ensuring your device remains invisible and inaccessible when enclosed.
Step 12: Stay Informed and Up-to-date
Follow Reputable Sources: Subscribe to blogs, podcasts, and YouTube channels focused on cybersecurity and privacy. Websites like The Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF), PrivacyTools, and Krebs on Security offer in-depth analysis and updates on the latest threats and protection strategies.
Use Educational Resources: Leverage platforms like Coursera, Udemy, or Khan Academy that offer courses on cybersecurity basics, digital privacy, and data protection. These can provide both foundational knowledge and insights into advanced topics.
Participate in Communities: Engage with online forums and communities such as Reddit’s r/privacy or XDA Developers. These communities can be excellent resources for advice, experiences, and recommendations on privacy tools and practices.
Tools and Examples:
RSS Readers: Apps like Feedly allow you to aggregate updates from your favorite cybersecurity news sources in one place, making it easier to stay informed.
Social Media: Following thought leaders and organizations dedicated to privacy and security on platforms like Twitter or X can provide timely updates and insights.
Privacy Badger and HTTPS Everywhere by EFF: Browser extensions that help protect your browsing privacy and secure your connections, developed by experts in digital rights.
Conclusion
In navigating the landscape of Android privacy and security, we've outlined a tiered approach that caters to varying levels of personal preference in privacy. From basic settings adjustments to adopting advanced security measures, Android provides a number of built-in security features and privacy options to protect your data on your phone. Emphasizing the importance of security apps for Android, including the role of Google Play Protect and smart lock security options, enhances security against common security problems many Android users face.
Android's operating system, from Android 11 to Android 12, continually evolves, offering updated privacy and security settings that require regular review. Utilizing tools like Norton Mobile Security adds an additional layer of security, safeguarding against evolving threats. As you run Android on your device, going through each setting, especially after security patches, ensures you're not only protected but also ahead of potential privacy concerns.
Remember, even when your phone is locked, vulnerabilities can exist. Therefore, secure lock settings and being cautious about whom you grant access to your phone are paramount. Whether it's signing in with Google, using security keys for authentication, or managing your Google account security through security checkups, your vigilance is your greatest ally.
Ready to take control of your digital privacy and security? Don't navigate the complex world of online data protection alone. Reach out to us at hello@mydataremoval.com or give us a call at (855) 700-2914 today. Let's safeguard your digital footprint together.


