Understanding the intricate balance between privacy and security in the realm of internet browsers has never been more crucial. Browsers are the primary tool through which we access the vast world of information on platforms like Google, YouTube, and Facebook.
However, not every browser is created equal, and saying this browser is better often misses the nuanced ways these tools affect our data privacy and security. From the data we download to the videos we stream, and the apps we use, our online activities are a goldmine of information, making it time for you to understand the risks and protections involved.
Whether it’s a single window on your device or an app on your phone, each connection, each mode of access, is a potential point of vulnerability. Yet, with the right knowledge about browser technology, antivirus software, privacy managers, and security systems, you can protect your digital footprint.
This article will be your guide to safeguarding your personal information across every platform, product, and content channel, ensuring that your experience is secure, private, and significant.
Strategies for Enhancing Browser Privacy and Security
I. The Double-Edged Sword of Browser Extensions
II. Tracking Technologies: Beyond Cookies
III. Hidden Risks in Security Features
IV. The Privacy Cost of Convenience
V. Understanding and Combating Browser Fingerprinting
I. The Double-Edged Sword of Browser Extensions
Browser extensions enhance functionality, personalizing your web experience by adding features that browsers don't include by default.
For example, ad blockers like AdBlock Plus or uBlock Origin can significantly improve your browsing experience by removing intrusive advertisements and potentially malicious adware.
Grammarly, another popular extension, assists with grammar and spelling suggestions in real-time, proving invaluable for both professional and casual writing.
However, the convenience of browser extensions comes with a privacy cost. Extensions have access to all your web activities, making it possible for them to track your browsing habits, collect data, or even inject malicious code.
For instance, a seemingly harmless extension for customizing your browser theme could be collecting data on your browsing habits and selling this information to third parties without your consent.
Quick Tips for Safer Extension Use:
Limit Your Extensions: Only install extensions that you need and use regularly. Each additional extension is a potential vulnerability, so keeping your list short minimizes risks.
Review Permissions: Before installing an extension, review the permissions it requests. Be wary of extensions that require access to all your data on websites or the ability to manage your downloads. If an extension's permissions seem too invasive for its functionality, consider looking for a safer alternative.
Regular Updates and Audits: Ensure your extensions are always updated. Developers frequently patch security vulnerabilities. Periodically review and remove extensions you no longer use.
Download from Official Sources: Always download extensions from the official browser web store and check reviews and ratings. Extensions like HTTPS Everywhere, from the Electronic Frontier Foundation, enhance security by enforcing HTTPS on sites you visit, illustrating the importance of choosing reputable sources.
Consider Privacy-Specific Extensions: Tools like Privacy Badger from the Electronic Frontier Foundation help block trackers and protect your browsing privacy. Another valuable tool, DuckDuckGo Privacy Essentials, not only blocks trackers but also provides site privacy ratings.
II. Tracking Technologies: Beyond Cookies
Beyond these well-known data collectors, web beacons and web workers play significant roles in monitoring our digital footsteps without our explicit consent.
Understanding these mechanisms is the first step toward regaining control of our online privacy.
Cookies are small pieces of data stored on your device by websites you visit, facilitating a more personalized web experience. However, they can also track your browsing activities across sites.
Web Beacons, also known as pixel tags or tracking pixels, are tiny, invisible images embedded within websites or emails. They notify the server when you have accessed content, making them a tool for stealthy surveillance.
Web Workers are JavaScript scripts that run in the background of a webpage, independent of user interaction. While designed to enhance website performance by executing tasks in the background, they can also persistently track users' activities even after closing a browser tab.
Simple Strategies to Limit Tracking
Use Privacy-Focused Browsers: Opt for browsers that are designed with privacy in mind, such as Brave or Firefox with its Enhanced Tracking Protection. These browsers offer built-in features to block cookies, web beacons, and fingerprinting techniques.
Install Anti-Tracking Extensions: Tools like Privacy Badger or Ghostery can detect and block tracking scripts from web beacons and web workers, giving you more control over what data you share.
Enable Do Not Track: Activate the 'Do Not Track' request in your browser settings. While not all websites honor this request, it signals your preference not to be tracked.
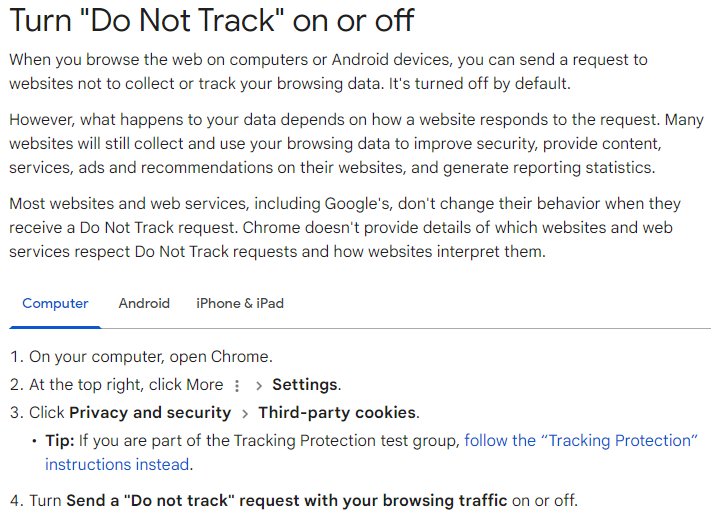
Regularly Clear Cookies and Cache: Make it a habit to clear your browser's cookies and cache regularly. This can help remove trackers that have been stored on your device. For a more seamless experience, use extensions like Cookie AutoDelete, which automatically clears cookies from sites you specify when you close the tab.
Use a Virtual Private Network (VPN): A VPN can mask your IP address, making it more difficult for trackers to pinpoint your location or link your online activities back to you. Reputable VPN services like NordVPN or ExpressVPN offer robust privacy protections.
III. Hidden Risks in Security Features
HSTS Super Cookies: A Privacy Paradox
HSTS is a policy mechanism that helps to secure websites against man-in-the-middle attacks by enforcing secure connections. However, it introduces a privacy risk through the use of "super cookies."
Unlike regular cookies, which can be easily managed and deleted by users, HSTS super cookies are much harder to remove and can be used by websites to track users persistently.
Use privacy-focused browsers like Brave or Firefox, which offer better control over HSTS tracking and easier ways to clear persistent storage that might contain super cookies.
Regularly use the browser's private or incognito mode for browsing sessions. While this doesn't prevent super cookies, it limits their long-term tracking capability.
Autofill Vulnerabilities: Convenience at a Cost
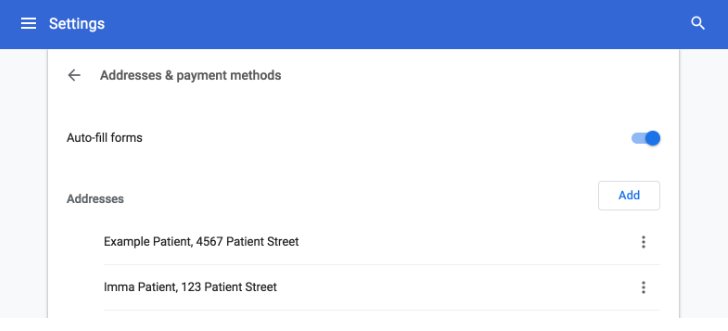
Autofill functionality speeds up the online experience by automatically completing forms with stored information, such as addresses and credit card numbers. However, this convenience can turn into a vulnerability.
Malicious websites can craft hidden forms to trick browsers into auto-filling data, which they then capture without the user's knowledge.
Disable autofill in your browser settings. For example, in Chrome, go to Settings > Autofill and turn off the options for passwords, payment methods, and addresses.
Consider using a dedicated password manager like Bitwarden. This tool offers more secure autofill options and provides additional layers of security, such as encrypted vaults and two-factor authentication, making them less susceptible to exploitation compared to browser-based autofill.
IV. The Privacy Cost of Convenience
The internet offers countless conveniences, from saving our passwords to auto-filling forms with a single click.
However, these conveniences come with a cost to our privacy. Let's delve into the trade-offs associated with autofill and password managers and how to navigate these features more securely.
Autofill: A Double-Edged Sword
Autofill saves time by completing forms with your personal information stored in your browser, including names, addresses, and even credit card numbers. While this feature is undeniably convenient, it also poses a risk.
Cybercriminals can design web pages with invisible fields to deceive browsers into filling out this sensitive information, which they then harvest.
Password Managers: The Secure Convenience
Password managers store your passwords in an encrypted database, offering a more secure alternative to the browser's autofill. They generate strong, unique passwords for each account, reducing the risk of breach.
However, they're not impervious to attacks. High-profile breaches have raised questions about storing all passwords in one place.
Additional Practices for Maintaining Privacy
Regularly Update and Monitor: Ensure your password manager is always up to date to benefit from the latest security patches. Regularly check your accounts for unauthorized access or breaches, a task some password managers can help automate.
Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): For an added layer of security, enable 2FA on your password manager and any online accounts that support it. This requires a second form of verification, such as a text message or an app, to access your account, significantly enhancing security.
V. Understanding and Combating Browser Fingerprinting
Browser fingerprinting is a tracking technique that collects information about your device and browser settings.
Fingerprinting gathers details like your screen resolution, browser version, installed fonts, and more, to create a unique profile of you.
This method is highly effective for tracking online behavior because it's difficult to alter enough of these attributes to change your digital fingerprint significantly.
Strategies to Reduce the Risk of Your Digital Footprint:
Use Privacy-Focused Browsers: Opt for browsers designed with privacy in mind, such as Brave or Tor Browser. These browsers have features that resist fingerprinting by blending your device’s profile with those of other users, making it harder to track you individually.
Install Anti-Fingerprinting Extensions: Tools like Privacy Badger and NoScript can help by blocking or managing scripts that websites use to fingerprint you. While no tool can make you completely untrackable, they can significantly reduce the amount of information you expose.
Limit or Disable JavaScript: Since fingerprinting scripts often rely on JavaScript, disabling it can thwart their efforts. However, this might break functionalities on some websites. A balanced approach is to use script management tools like NoScript, allowing JavaScript only on trusted sites.
Adjust Your Browser’s Privacy Settings: Increase your privacy level by adjusting settings in your browser. For instance, enabling “Do Not Track” and disabling third-party cookies can help, even if not all websites honor these preferences.
Regularly Clear Your Browser Data: Although this doesn't directly combat fingerprinting, regularly clearing your browser cache, cookies, and history can prevent trackers from correlating collected data over time. Automated tools like CCleaner can help manage this process.
VI. Embracing Browser Isolation
Browser isolation is a powerful strategy to enhance your online privacy and security. It involves using different browsers for different activities to compartmentalize your online identity and activities.
This approach can significantly reduce the risk of cross-site tracking and personal data leaks.
How Browser Isolation Works:
Separate Activities Across Browsers: Use one browser for social media and another for general browsing. You might choose a third for sensitive activities like online banking. For instance, use Firefox for daily activities, Chrome for YouTube and social media, and Brave for financial transactions.
Dedicated Browser for Sensitive Tasks: Consider using a browser like Tor for highly sensitive or private searches. Tor anonymizes your internet activity, making it hard to trace back to you.
Basic Setup for Personal Use:
Choose Your Browsers: Select a primary browser for everyday use and secondary browsers for specific activities. Privacy-focused browsers like Brave or Firefox are excellent for everyday browsing due to their built-in privacy protections.
Configure Privacy Settings: In each browser, go into the settings and adjust the privacy controls. Enable features like tracking protection, block third-party cookies, and use private browsing modes as defaults if possible.
Use Privacy Extensions: Equip each browser with privacy-enhancing extensions. uBlock Origin for ad blocking, HTTPS Everywhere for secure connections, and Privacy Badger for blocking trackers are essential.
Isolate Social Media: Use one browser exclusively for social media platforms to prevent them from tracking your activities across other sites. Make sure to log out from these platforms when done, even in the dedicated browser.
Regular Maintenance: Regularly clear cookies and browsing history in each browser. Consider using a tool like CCleaner for routine maintenance, or set your browsers to automatically clear data upon closing.
VII. Selecting Privacy-Enhancing Tools
In an era where online privacy is constantly under threat, employing tools to safeguard your digital footprint is crucial. Among the myriad of options available, VPNs and privacy-focused browsers stand out for their effectiveness in enhancing online privacy.
VPNs (Virtual Private Networks):
VPNs encrypt your internet connection, hiding your online activities and location from ISPs, governments, and potential snoops. They are essential for securing connections, especially on public Wi-Fi networks.
NordVPN and ExpressVPN are renowned for their strong encryption protocols, no-logs policies, and extensive server networks.
ProtonVPN known for its security focus, offers a free tier with limited speeds but exceptional privacy.
Privacy-Focused Browsers:
These browsers are designed to block trackers, ads, and other invasive scripts by default, providing a more private and secure browsing experience without additional configurations.
- Brave offers built-in ad and tracker blocking
- Firefox offers significant privacy controls.
- Tor Browser provides anonymity by routing your traffic through multiple nodes worldwide.
Criteria for Choosing Privacy Tools:
Privacy Policies: Opt for tools with strict no-logs policies. Ensure they don't store or sell your data by reading their privacy policies thoroughly.
Security Features: Look for features like AES-256 encryption for VPNs, HTTPS Everywhere, and tracker blocking in browsers. Additional features like kill switches in VPNs enhance security by cutting off internet access if the VPN connection drops unexpectedly.
Performance: While privacy is paramount, usability shouldn't be compromised. Choose tools that offer fast connection speeds (for VPNs) and smooth browsing experiences (for browsers) to avoid frustration.
User Reviews and Reputation: Research and consider the community feedback and expert reviews. A longstanding positive reputation is a good indicator of reliability and effectiveness.
Ease of Use: The tool should be user-friendly, with a straightforward interface and easy setup process. This ensures that you can maximize its privacy features without needing extensive technical knowledge.
Compatibility: Ensure the tools work across your devices and platforms. Consistent protection across your smartphone, tablet, and computer is crucial for comprehensive privacy.
Conclusion
Navigating the web safely is like picking the best gear for a deep-sea dive. You need the right tools—not just any browser will do. Understanding that there are flaws in every single browser helps us see how deeply our choices can impact our privacy. Whether you're scrolling on your Android, tapping away on your iPhone, or clicking through pages on your PC, picking the right browser is crucial.
From Chrome’s extensive features to Firefox's community-driven development, and from Brave’s ability to block ads to Edge’s seamless integration with Microsoft, each browser offers unique advantages. However, it’s crucial to note that no browser is flawless. For those who prioritize privacy above all, Tor provides the highest level of security, albeit with some challenges in personalizing the experience.
Using a VPN is like having a secret passage through the internet. It keeps your online footsteps hidden, wrapping your data in a layer of encryption. Tweaking your DNS settings is another stealth move, keeping unwanted trackers at bay.
Staying secure online isn’t solely about the browser you choose; it’s about being astute with the settings, recognizing the importance of a reliable VPN, and consistently defending against malware. It’s about making educated decisions, aware that even minor details, like your IP address or geographical location, are significant.
Elevate your online privacy with MyDataRemoval. For expert guidance on secure browsing and more, email us at hello@mydataremoval.com or call (855) 700-2914. Secure your digital world today!


